Ideje 96 Atom Quantum Theory
Ideje 96 Atom Quantum Theory. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.
Nejchladnější Quantum Mechanical Model Of The Atom Part 01 Youtube
The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. This is known as the uncertainty principle.Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:
An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. This is known as the uncertainty principle. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).

Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry.

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms.

This is known as the uncertainty principle. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry... Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …

Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction... Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time.

Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron.

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms.. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element.

The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry... Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.

Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom.. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. This is known as the uncertainty principle. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).

The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element.

According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom.. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. This is known as the uncertainty principle. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms... Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction.. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

Nuclear reactions can alter atoms... Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.

They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. This is known as the uncertainty principle. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce... Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.

The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta.

An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).
Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle... The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. This is known as the uncertainty principle. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce.
According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time... Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron.

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.

May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means.. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry... The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron.

This is known as the uncertainty principle.. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects... According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time.
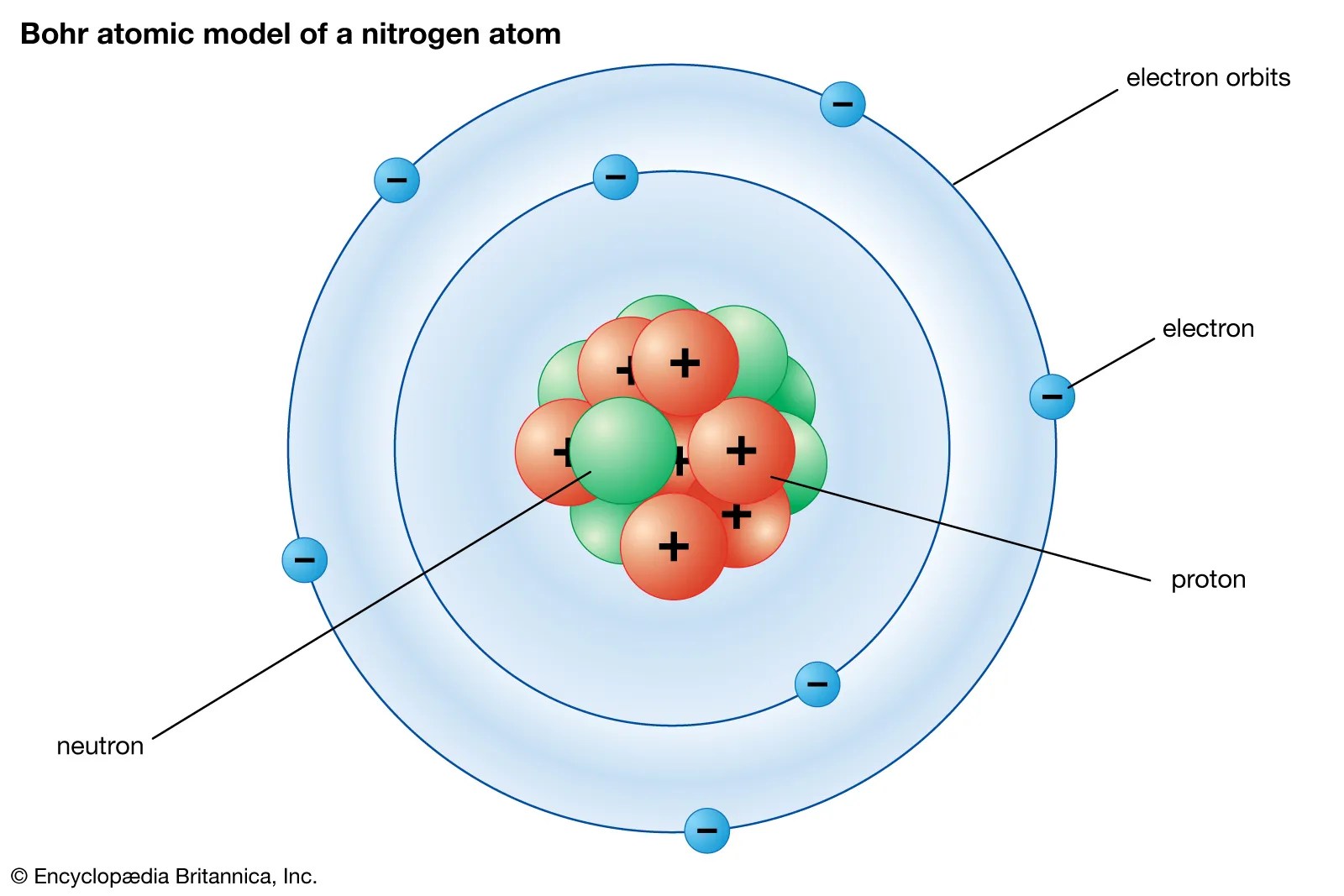
Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle... They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).

The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged)... They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. This is known as the uncertainty principle. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means.

Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta... The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged)... Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric ….. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Nuclear reactions can alter atoms.

Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce.

May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time.
Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric ….. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.

May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

This is known as the uncertainty principle. This is known as the uncertainty principle. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means.. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction.
Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle... Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).

The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron.. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.
As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …

An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: This is known as the uncertainty principle. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry... The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce.

They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom.. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms... As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. This is known as the uncertainty principle.

Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time.

Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron.. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means.
Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta... Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction.. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time.

Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …

The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across... The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).

Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction.

The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged).. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. This is known as the uncertainty principle. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. The quantum numbers \(n, \ l, \ m\) are not sufficient to fully characterize the physical state of the electrons in an atom.

As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.

Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time.

An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron.

Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction.

Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric ….. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller.

This is known as the uncertainty principle.. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta.. The concept of the atom that western scientists accepted in broad outline from the 1600s until about 1900 originated with greek philosophers in the 5th century bce.

Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Nuclear reactions can alter atoms.. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry.

An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element.every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The three parts of the atom are protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral charge), and electrons (negatively charged). According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Their speculation about a hard, indivisible fundamental particle of nature was replaced slowly by a scientific theory supported by experiment and mathematical deduction. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. Niels bohr and max planck, two of the founding fathers of quantum theory, each received a nobel prize in physics for their work on quanta. May 06, 2019 · an atom is a building block of matter that cannot be broken apart using any chemical means. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects. This is known as the uncertainty principle. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across.. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric …

Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element.. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics—as if they were tennis balls, for example—is not possible due to quantum effects.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom uses complex shapes of orbitals (sometimes called electron clouds ), volumes of space in which there is likely to be an electron. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism.according to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Einstein is considered the third founder of quantum theory because he described light as quanta in his theory of the photoelectric … According to quantum theory, it's impossible to know the exact position and momentum of an electron at the same time. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.